Restoring Specular-Free Video Sequences from Rank-Constrained Data
Image courtesy of Samar Alsaleh (George Washington University), Angelica Aviles-Rivero, James Hahn (George Washington University)
Researchers: Samar Alsaleh (George Washington University), Angelica Aviles-Rivero, James Hahn (George Washington University)
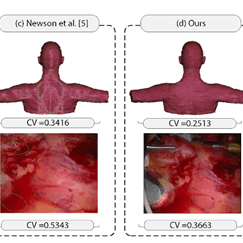
Minimally invasive surgical and diagnostic systems are commonly used in clinical practice. However, accuracy and robustness of these systems depend heavily on computer based processes such as tracking, detecting and segmenting clinically meaningful regions of interest, which are significantly affected by the inherent specular reflections that appear on the organs’ surface. Restoration of the acquired data for clinical purposes still present challenges because of the high texture and color variation across the image, which leads to over-estimation and slow convergence. In this project, we pose the question – How to achieve a realistic image restoration while keeping a trade-off between computational time and accuracy? We respond to this question by setting the basis for achieving a realistic approximation of the damaged images with the objective of improving minimally invasive surgeries and diagnostic systems. We also demonstrate that our solution deals with complex cases such as strong illumination variation and big damaged areas through a careful quantitative evaluation.
